DigiCert root certificate upgrade guide
This guide aims to assist you in correctly installing and configuring the DigiCert Global Root G2 root certificate, ensuring that your system or app can properly recognize SSL/TLS certificates issued by this root certificate.
1. Check the compatibility
The DigiCert Global Root G2 root certificate is widely supported across mainstream operating systems and environments, with the minimum compatible versions as follows:
| Root certificate name | Root certificate serial number | Windows | Mac OS | Android | iOS | Mozilla | Java |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DigiCert Global Root G2 | 03:3A:F1:E6:A7:11:A9:A0:BB:28:64:B1:1D:09:FA | Windows XP SP3+ | Mac OS X 10.10+ | Android 5.0+ | iOS 7.0+ | Firefox 32+ NSS 3.16.3 | JRE1.8.0_131+ |
If the environment that you use encounters certificate trust issues, follow the steps below to upgrade your root certificate.
2. Download the root certificate
Select the appropriate format for your system to download the root certificate:
For detailed information about the DigiCert Global Root G2, visit the DigiCert official website.
3.Upgrade the root certificate
By the operating system
Linux systems
The location where the system stores trusted root certificates varies by distribution. Typically, root certificates are stored in the /etc/ssl/certs/ directory or in the /etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt file.
- CentOS
# Install the certificate management tool
yum install -y ca-certificates && update-ca-trust
# Copy the root certificate
cp DigiCertGlobalRootG2.crt.pem /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/DigiCertGlobalRootG2.crt
# Update the certificate
update-ca-trust extract
# Verify the installation
grep -inr 'pLiaWN0bfVKfjllDiIGknibVb63dDcY3fe0Dkhvld1927jyNxF1WW6LZZm6zNTfl' /etc/pki/
- Ubuntu/Debian
# Install the certificate management tool
apt-get install -y ca-certificates
# Copy the root certificate
cp DigiCertGlobalRootG2.crt.pem /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/DigiCertGlobalRootG2.crt
# Update the certificate
update-ca-certificates
# Verify the installation
grep -inr 'pLiaWN0bfVKfjllDiIGknibVb63dDcY3fe0Dkhvld1927jyNxF1WW6LZZm6zNTfl' /etc/ssl/certs/
- Alpine
# Install the certificate management tool
apk add --no-cache ca-certificates
# Copy the root certificate
cp DigiCertGlobalRootG2.crt.pem /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/DigiCertGlobalRootG2.crt
# Update the certificate
update-ca-certificates
# Verify the installation
grep -inr 'pLiaWN0bfVKfjllDiIGknibVb63dDcY3fe0Dkhvld1927jyNxF1WW6LZZm6zNTfl' /etc/ssl/certs/
Windows systems
- Install the
DigiCertGlobalRootG2.crtroot certificate.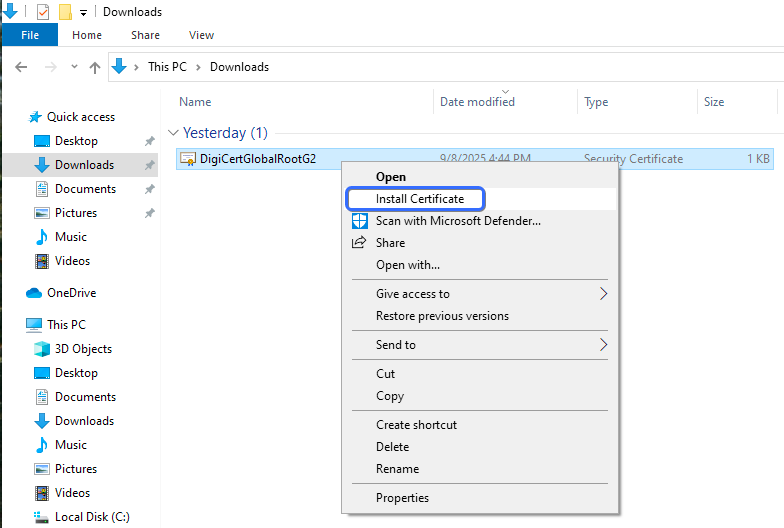
- Select the Trusted Root Certification Authorities as the storage location.
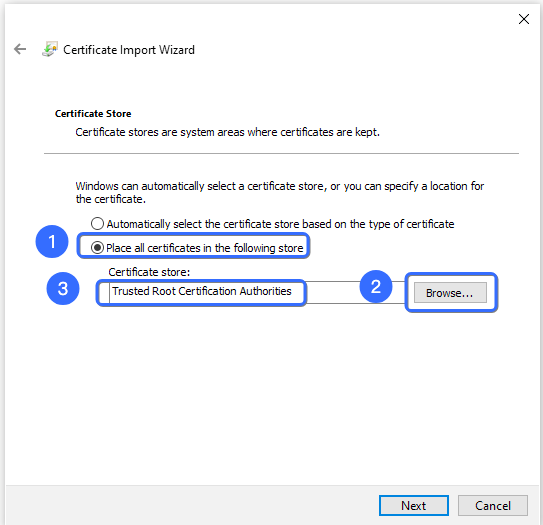
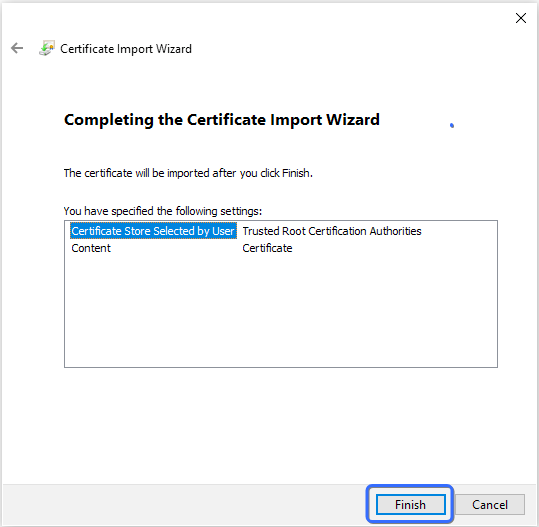
- Click Finish to complete the import process successfully.
- Open Command Prompt (CMD) and enter
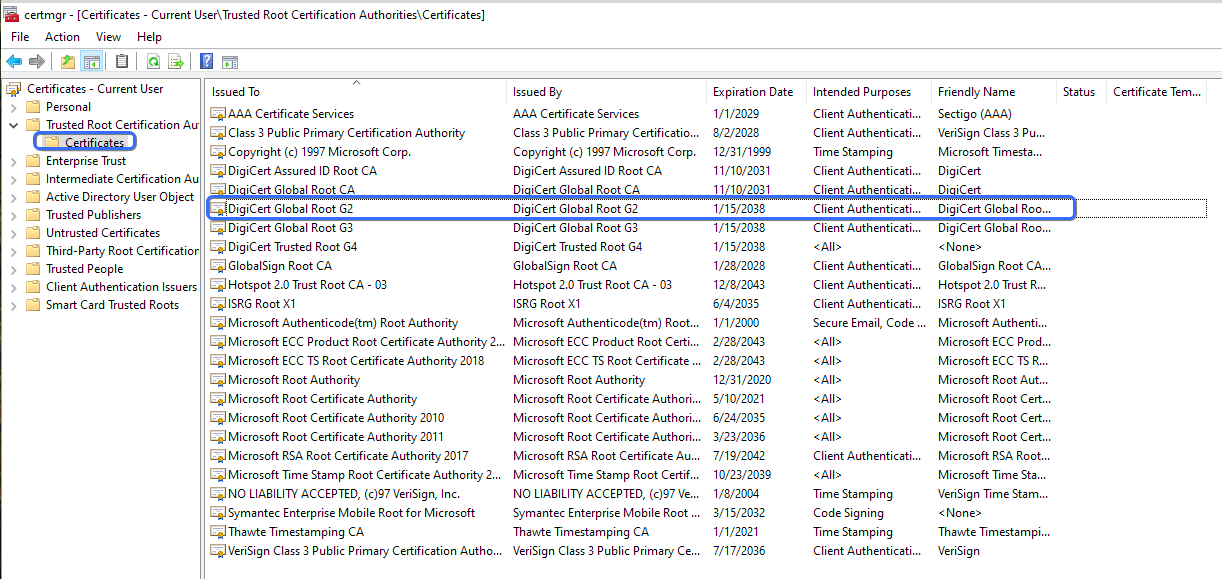
certmgr.mscto access the certificate manager.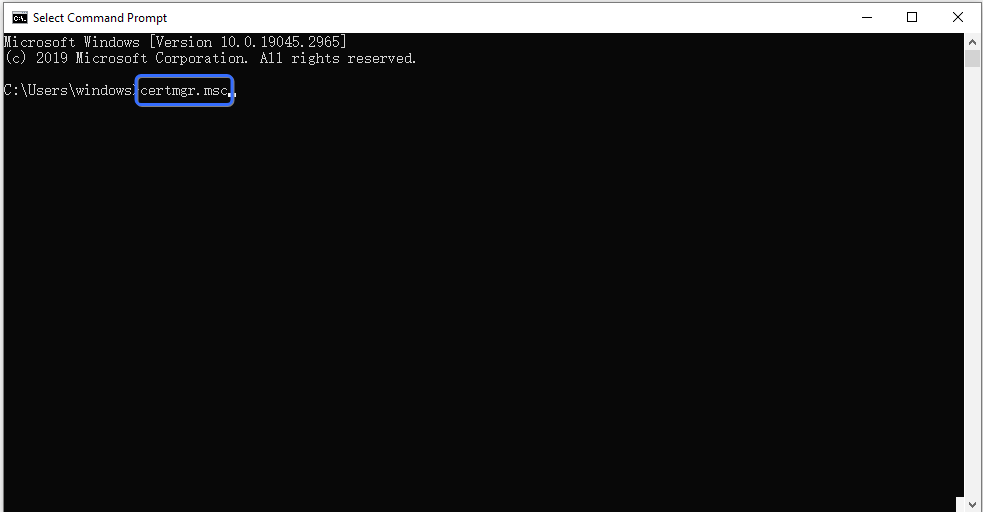
- Locate the DigiCert Global Root G2 certificate under Trusted Root Certification Authorities to confirm successful installation.
macOS systems
Method 1: GUI installation
- Open the root certificate
DigiCertGlobalRootG2.crt.pem.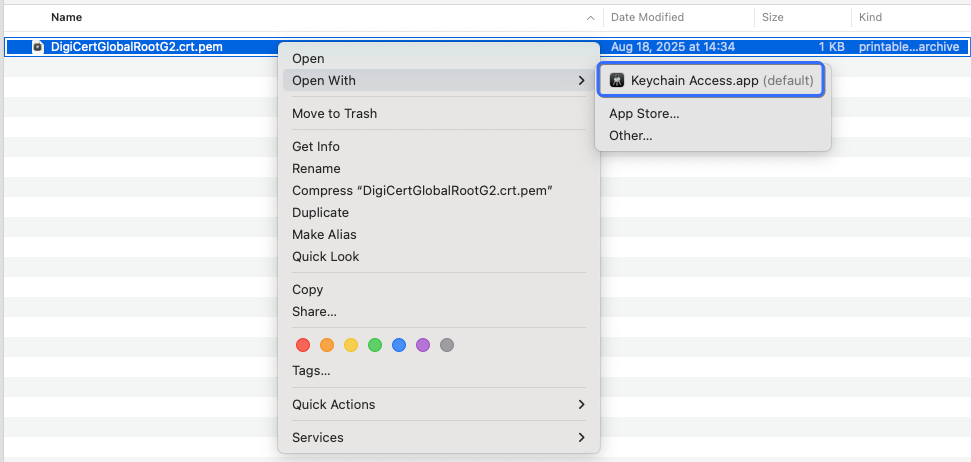
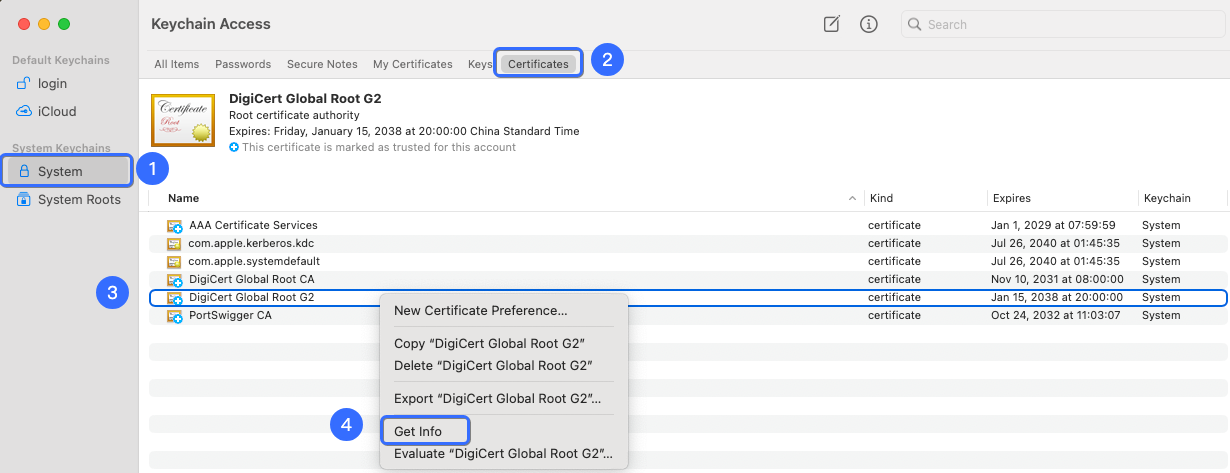
- Locate the certificate in Keychain Access, and open it by clicking Show Info.
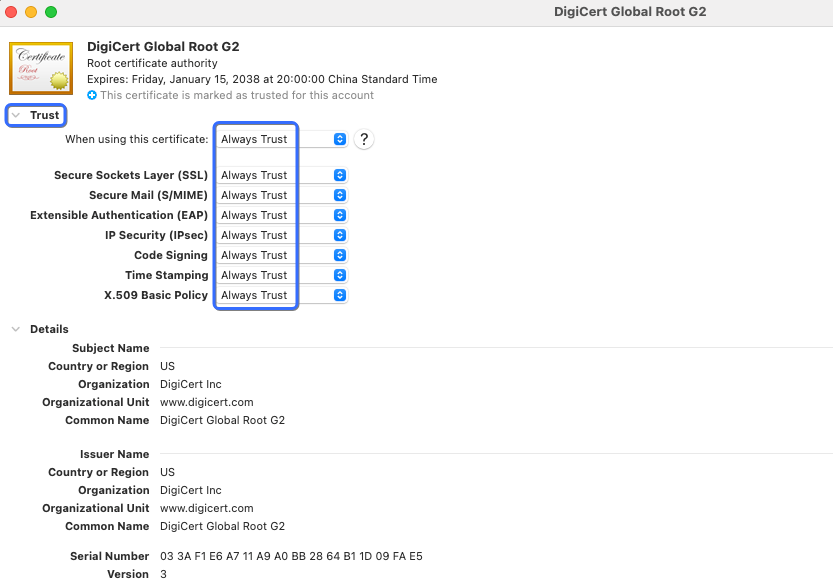
- Set the certificate's trust settings to Always Trust.
Method 2: Using Homebrew-installed curl/openssl
# Append the certificate to the trust file
cat DigiCertGlobalRootG2.crt.pem >> /usr/local/etc/ca-certificates/cert.pem
# Verify the installation
grep -in 'pLiaWN0bfVKfjllDiIGknibVb63dDcY3fe0Dkhvld1927jyNxF1WW6LZZm6zNTfl' /usr/local/etc/ca-certificates/cert.pem
By the development environment
Java
Method 1: Manually import to cacerts
Use the keytool command to upgrade the root certificate. The DigiCertGlobalRootG2.crt.pem`` is the PEM format root certificate file, and DigiCertGlobalRootG2` is the alias for the root certificate.
keytool -importcert -alias DigiCertGlobalRootG2 -file DigiCertGlobalRootG2.crt.pem -keystore $JAVA_HOME/lib/security/cacerts
Method 2: Upgrade JDK
If using an older JDK version (such as JDK 1.6 or 1.7), it is recommended to upgrade to JDK 8 or higher.
PHP
In PHP code, specify the root certificate path:
curl_setopt(pCurl, CURLOPT_CAINFO, "./DigiCertGlobalRootG2.pem ");
Python
If you encounter an error message like SSL: CERTIFICATE_VERIFY_FAILED when making requests with Python, it indicates incompatibility and requires upgrading the root certificate.
- If Python is set to use the trust root certificate store from the system's ssl module (typically OpenSSL), upgrade the root certificate by the operating system.
- If you want to manage the root certificate store independently, refer to the Python 2.7 ssl documentation or Python 3 ssl documentation.
4.Verify the upgrade
To verify whether the root certificate has been successfully upgraded, you can use any one or more of the following methods. The following example uses the store URL https://{handle}.myshopline.com/admin to demonstrate different verification approaches, where handle represents the store's semantic identifier.
Caution: For root certificates updated using development environments such as JAVA, PHP, and Python, you need to manually validate the update within your code.
Browser access
When you visit a store URL, such as https://{handle}.myshopline.com/admin, if the page loads without a certificate error message, the installation is successful.
Using curl to verify
Use the curl command to access a URL, such as https://{handle}.myshopline.com.
curl -v --tlsv1.2 -o /dev/null -s --max-redirs 0 'https://{handle}.myshopline.com'
If the output contains SSL certificate verify ok, the certificate upgrade is successful.
If the output states SSL certificate problem: unable to get local issuer certificate, the root certificate upgrade failed.
Using OpenSSL to verify
Use the openssl command to access a URL, such as https://{handle}.myshopline.com.
timeout 5 bash -c "true | openssl s_client -tls1_2 -connect {handle}.myshopline.com:443 -servername {handle}.myshopline.com -showcerts"
If the output matches the following expectations, the root certificate upgrade is successful.
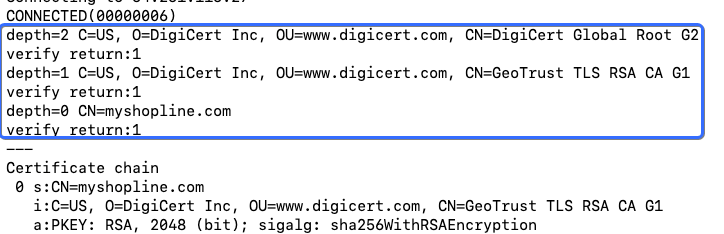 If the output includes
If the output includes error:num=20:unable to get local issuer certificate, the root certificate installation failed.